Author
Nigel Payne - Flat Roof Specialist
Essential Fire Safety Measures for Flat Roofs: Protecting Your Building from Potential Hazards
Everyone knows the importance of fire safety. With the possibility of fires escalating in an instant and putting lives and the integrity of a property in danger, reducing this risk is of the utmost importance. Unfortunately, for those with flat roofs, it is easier for a fire to spread, so knowing the right precautions and strategies is vital to combat and prevent fires on flat roofs straightaway. In this blog, we will be explaining everything from the risks to fire-resistant roofing materials and much more. So, let’s get started.
Potential Risks And Challenges Associated With Flat Roofs In Terms Of Fire Hazards
Although many people like the look of flat roofs, or even need them due to necessity, you should be aware of some of the potential risks associated with them when talking about fire hazards.
Fire Spreading From an Adjacent Property
When a fire breaks out in an adjacent property, particularly if it is close to a building with flat roofs, there is a genuine risk that the flames can extend to the external surfaces of these structures. The open expanse of a flat roof can provide an easy pathway for fire to travel and wreak havoc on neighbouring buildings.
Fire Spreading From One Internal Compartment to Another
Another common fire risk for flat roofs is fire spreading from one internal compartment under the roof to another. Things like vents and ducts make it easy for a fire to spread from one internal compartment to another. Thermal updrafts, created by the heat and smoke rising from the fire, play a crucial role in fire spreading through the roof. As hot air builds, it looks for a way out. This increase in oxygen fuels the fire, increasing its heat and allowing it to breach the roof. Once it does this, it can rapidly spread beneath the roof structure, hidden from view but causing damage to neighbouring compartments.
Hot Works During Installation of Flat Roof
Hot works are a great method for installing flat roofs, but when done incorrectly, it could lead to a big fire hazard. The open flames or hot air involved in hot works pose a significant fire risk. The extreme heat can ignite flammable materials in the vicinity, leading to a potentially devastating fire. If not handled carefully, hot works can cause damage to the existing roof structure, insulation or adjacent materials. Because of this, it’s always a good idea to choose contractors who have extensive experience with performing hot works to ensure none of these risks occurs.
Using Combustible Materials
Many cost-effective and long-lasting materials, such as asphalt and bitumen, are fantastic for many roofs, but they are combustible. Despite their advantages, combustible materials pose a potential risk in the event of a fire. If not adequately protected, they can ignite and contribute to the rapid spread of flames, potentially endangering both the property and its occupants. By installing them correctly and following all fire safety best practices, they can still be used on many roofs and are unlikely to be too much of a risk.
Difference Between BS EN 13501-1 and BS EN 13501-5
BS EN 13501-1 is a fire classification test designed to evaluate the reaction to fire of construction products and materials. This test assesses the performance of individual components used in flat roofs, such as insulation and other materials. The objective is to determine their response to fire, including factors such as combustibility, ignitability, and more. While the BS EN 13501-1 test focuses on individual components, the BS EN 13501-5 test evaluates the fire performance of the complete flat roof build-up. It assesses how the various components interact with each other in the event of a fire, considering factors such as fire spread, flame penetration, and the potential for fires to build.
How Combustible Materials Can Be Used in the Build Up
To meet the BS EN 13501-5 rating, where combustible materials can be used (anything less than A1 according to the BS EN 13501-1 test), the entire roofing system should undergo rigorous testing as a whole. This test ensures that even if individual components are combustible, the overall system will have the required level of fire resistance. Take a look at this table to get a better understanding of how to achieve the appropriate ratings per the BS EN 13501-5 test:
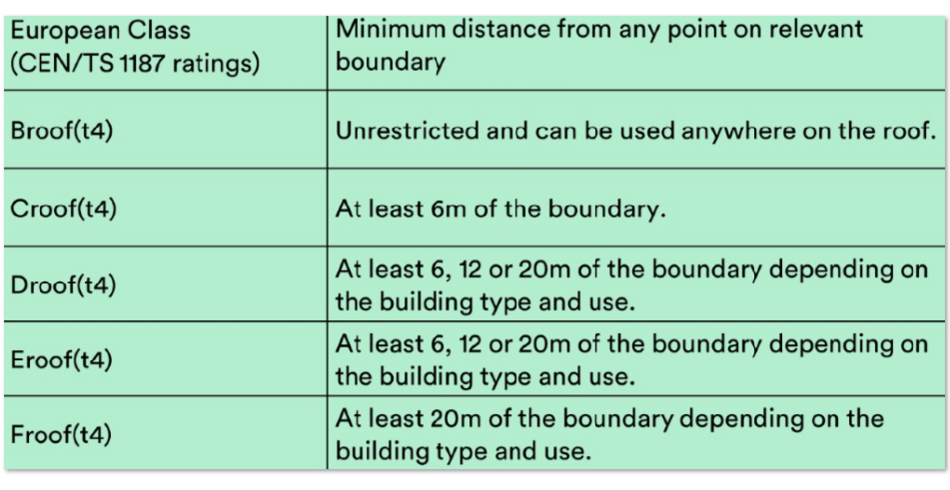
Why Proper Insulation and Ventilation in Fire Safety is Vital
Insulation and ventilation are two critical aspects of fire safety in any building, including those with flat roofs. Here's why:
Slowing Down the Spread of Fire
Proper insulation helps slow the spread of flames during a fire. It acts as a barrier, limiting the fire's ability to reach other areas of the building. By reducing the rate of fire spread, insulation can provide time for evacuation.
Limiting Structural Damage
In addition to slowing the spread of fire, insulation helps prevent structural damage. Flat roofs are vulnerable to intense heat, and without adequate insulation, the high temperatures can cause the structural elements of the roof to weaken or even collapse. Proper insulation can mitigate this risk by maintaining lower temperatures and preserving the roof's integrity for a longer period. Now that we understand the significance of insulation and ventilation in fire safety, let's look at how specific materials and techniques can help prevent the spread of fire:
Fire-Resistant Insulation Materials
Choosing insulation materials with excellent fire-resistant properties is crucial. Mineral wool, glass wool and certain types of foam insulation are commonly used due to their high fire resistance. These materials can withstand high temperatures, effectively reducing the spread of flames and minimising smoke production.
Proper Ventilation Systems
While insulation plays a vital role in fire safety, ventilation is equally important. Properly designed ventilation systems ensure the release of smoke, heat, and toxic gases from the building. This helps prevent the build-up of flammable gases and minimises the risk of an intense fire.
What’s The Importance of Compartmentalisation?
Compartmentalisation is where you divide a building into separate compartments, each with its own fire-resistant walls and floors. This strategy aims to limit the spread of a fire, confining it to a specific area and buying crucial time for evacuation and firefighting efforts. But that’s not all it does. Compartmentalisation not only restricts the spread of fire but also contains smoke and toxic gases from reaching other rooms. This containment keeps escape routes clearer, helping people evacuate faster and reducing the risk of occupants inhaling smoke.
To Wrap Up
All in all, understanding and implementing essential fire safety measures for flat roofs is crucial for protecting your building from potential hazards. By recognising the fire risks and taking the right steps, you can enhance the safety of your flat roof property. It’s always a good idea to research the fire rating tests to properly understand exactly what they are and what is required, as well as adhere to the regulations set out in Approved Document B and Building Bulletin 100. This way, you can best protect your flat-roof buildings from the risk of fire hazards. To find out more about fire safety measures for flat roofs, contact us today.



